RESTRICT and EXTEND rules
When you define a record level security formula, you define RESTRICT rules and EXTEND rules.
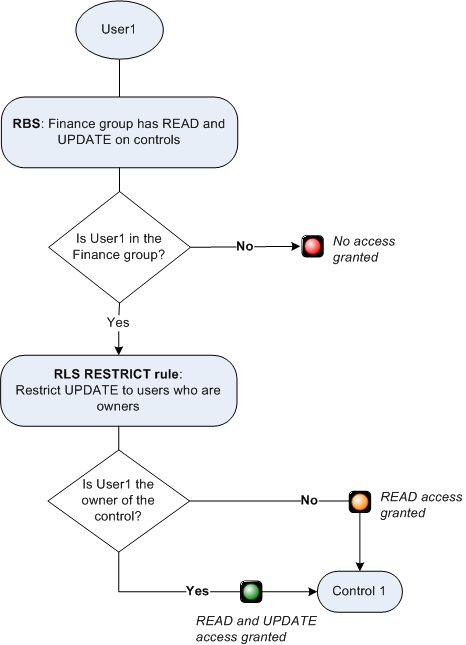
A RESTRICT rule is applied after role-based security (RBS). A RESTRICT rule further restricts access to an object. The following formula illustrates how a RESTRICT rule is evaluated:
If (RBS=True AND RESTRICT_RULE_RESULT=True), then grant accessNotice the AND operator. Role-based security must grant access, and the result of the RESTRICT rule must be true. The result is that users get access to the object if role-based security grants them access and the RESTRICT rule result is also true.
For example, suppose role-based security grants all users in the Finance group READ and UPDATE
access on Control objects. But, you want users to be able to do an UPDATE only if they are also the
owner of the control object. In this case, you can add a RESTRICT rule on UPDATE that checks the
END_USER against the owner field of the object.
For a more detailed example, see the record level security scenarios, such as Scenario: Objects that are shared across GRC domains.
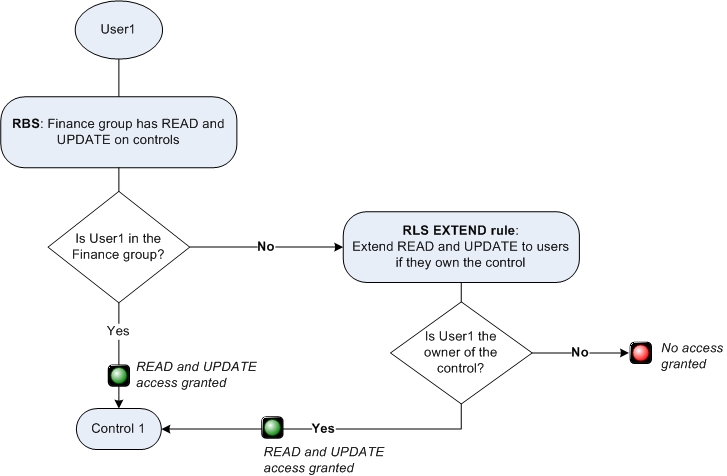
An EXTEND rule is applied in addition to role-based security. An EXTEND rule grants access to an object for which role-based security does not grant access. The following formula illustrates how an EXTEND rule is evaluated:
If (RBS=True OR EXTEND_RULE_RESULT=True), then grant accessNotice the OR operator. Either role-based security must give access or the EXTEND rule result must be true. The result is that users get access to the object if role-based security gives them access or if the EXTEND rule result is true. Which means users gain access to the object in all of the following scenarios:
- Role-based security is granted and the EXTEND rule result is true, OR
- Role-based security is granted and the EXTEND rule result is false, OR
- Role-based security is not granted and the EXTEND rule result is true.
For example, suppose role-based security grants all users in the Finance group READ and UPDATE
access on Control objects. However, you also want users to be able to READ and UPDATE if they are
the owner of the control object, regardless of whether they belong to the Finance group. In this
case, you can add an EXTEND rule on READ and UPDATE that checks the END_USER
against the owner field of the object.
For a more detailed example, see the record level security scenarios, such as Scenario: Access for business administrators.
Whether you are using a RESTRICT rule or an EXTEND rule, the rule is evaluated within the context of role-based security.