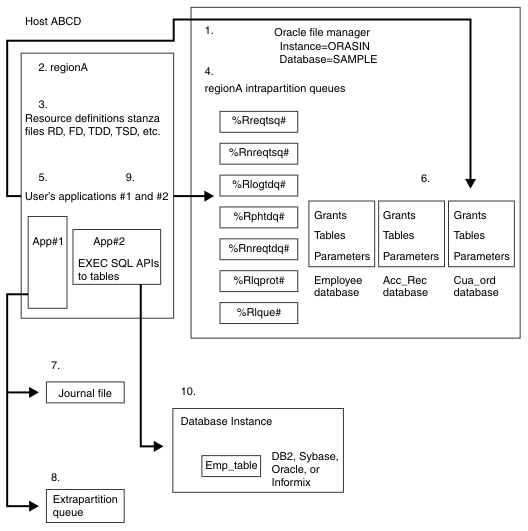
Figure 1 shows how a CICS system uses files and queues. The example CICS system that is shown in this diagram resides on a host machine that is identified as hostABCD. An Oracle database, named SAMPLE, is acting as the file manager for this system. This Oracle file manager and instance, named ORASID, is managing files and queues for regionA. In this example, the user has created an application, App#1, on regionA that stores its data in Oracle tables that are managed by the Oracle file manager, ORASID. This application also uses a journal file and an extrapartition queue, neither of which is managed by the Oracle file manager. Instead, these files are managed by the operating system file structure.
In addition, on regionA, the user is using a relational database application, App#2, to access data that is stored in tables. The relational database product can be any of the four that are supported by CICS: DB2®, Oracle, Sybase, or Informix®. The Oracle file manager does not manage the relational database's tables. That job is done by the database product itself.
This section uses the numbered areas that are shown in Figure 1, to discuss the ways in which a CICS system, created by CICS control program commands, can make use of files and queues. The pertinent CICS commands, resource definitions, and Oracle commands that are related to the area are described.
- The Oracle file manager, an instance identified as ORASID, is shown in Area 1. The file manager must exist and must be running before the region that is to use it is created. The file manager can be created by issuing the Oracle commands that are described in Preparing for Oracle file and queue management.
- When the file manager is running, the region that is to use it can be created. Area 2 shows a region named regionA. If the user follows the instructions that are given in Configuring and starting your first TXSeries region, the command cicscp -v create region regionA -o ORACLE -u cics/cics is issued. The -o option is required to identify the instance; the default database for the instance ORASID is used; the -v option provides for verbose output from the command. When the user issues this command, the resource definition stanza files, shown in Area 3, and the intrapartition queues, shown in Area 4, are automatically created. The cicscp start region regionA command activates the region and connects it to the Oracle file manager.
- Area 3 shows the file structure that is created to hold the resource definitions for regionA. The resource definition file structure is automatically created when the cicscp create region command is issued. The user adds a resource definition entry for each resource that is available to the CICS system. (Resource definition classes identifies the classes of resource definitions and describes the CICS resource management commands that are used to create these definitions.)
- Area 4 shows the intrapartition queues that are automatically created by the cicscp create region command. The %R prefix that is attached to each queue name expands to the name of the region. In this example, it expands to regionA. The number sign (#) suffix that is attached to each queue name indicates a table in the Oracle database. Of these seven queues, only the %Rnreqtdq# queue can be accessed without the addition of a resource definition entry to identify it to the CICS system. The %Rlogtdq#, the %Rphtdq#, the %Rlque, and the %Rlqprot# queues must be named in a Transient Data Definition (TDD) stanza file. The %Rnreqtsq and the %Rreqtsq queues must be declared in a Temporary Storage Definition (TSD) stanza file. When the TDD or TSD entry is made, CICS can use the CICS application programming interface (API) commands to access these queues.
- Area 5 shows an application, App#1, that uses EXEC CICS APIs to access Oracle tables that are managed by the Oracle file manager. The application is identified to CICS through a Program Definition (PD) entry in the PD stanza file.
- Area 6 shows the Oracle tables that hold the data for the user's application, App#1. The application's data tables are defined to CICS through a File Definition (FD) and accessed through EXEC CICS API commands in the application.
- Area 7 shows a journal file that is used by App#1, identified in Area 5. A journal file is not managed by the file manager. It is an ASCII file that is managed by the operating system's file structure. It is identified to CICS by a Journal Definitions (JD) entry and accessed through EXEC CICS API commands that are embedded in the application.
- Area 8 shows an extrapartition queue that is used by App#1, which is identified in Area 5. An extrapartition queue is not managed by the file manager. It is an ASCII file that is managed by the operating system's file structure. It is identified to CICS by a TDD entry and accessed through EXEC CICS API commands that are embedded in the application.
- Area 9 shows a relational database application, created by the user, that resides on regionA. This application uses EXEC SQL commands to access database tables that reside in the operating system's file structure. The application is identified to CICS through a Program Definition (PD) entry in regionA's PD stanza file.
- Area 10 show the database tables that hold the data for the application identified in area 9. These tables are managed entirely by the database product. FD entries are needed to identify these tables to CICS.
The Oracle configuration procedures that are described here set the following resource definition attributes:
- Region Definitions (RD)
- FileSystemType is set to ORACLE.
- DefaultFileServer is set to the name of the oracle instance that is used for queue and file management for the region that is picked up from the environment variable ORACLE_SID.
- RDBMSInstance is set to the name of the instance that is used for queue and file management for the region that is picked up from the environment variable ORACLE_SID.
- Product Definitions (XAD)
- XAOpen is set to the string that is used to connect to the database.
- SwitchLoadFile is set to a string that points to an object file
that contains the xa_switch_t structure definition and XA-support subroutines
for Oracle. Note: You must use your own switch load files, as described in Preparing for Oracle file and queue management.