Secure Sockets Layer and Transport Layer Security communication
You can use the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol to provide transport layer security for a secure connection between IBM Spectrum Protect™ servers, clients, and storage agents. If you send data between the server, client, and storage agent, use SSL or TLS to encrypt the data.
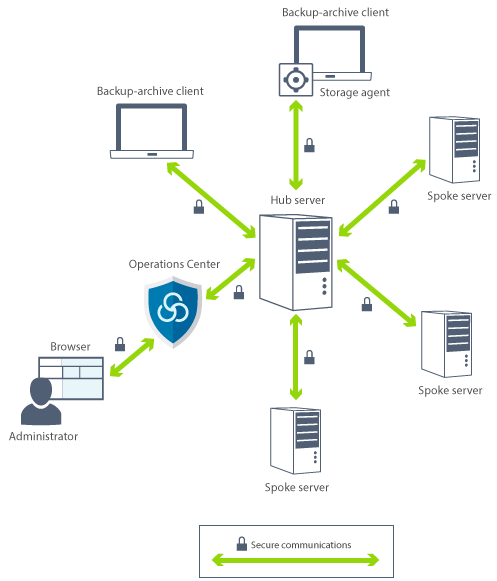
SSL and TLS are provided by the Global Security Kit (GSKit) that is installed with the IBM Spectrum Protect server that the server, client, and storage agent use. The Operations Center and Reporting agent do not use GSKit.
Each IBM Spectrum Protect server, client, or storage agent that enables SSL must use a trusted self-signed certificate or obtain a unique certificate that is signed by a certificate authority (CA). You can use your own certificates or purchase certificates from a CA. Either certificate can be installed and added to the key database on the IBM Spectrum Protect server, client, or storage agent.
If you use a root certificate from a CA, you must install it on each key database for the client, server, and storage agent that initiates SSL communication. A root certificate is certificate that identifies the Root Certificate Authority. The certificate is verified by the SSL client or server that requests or initiates the SSL communication.
Configure SSL or TLS independently on the IBM Spectrum Protect server, client, and storage agent.
The IBM Spectrum Protect server, client, or storage agent can serve as SSL clients during communication. An SSL client is the component that initiates communication and verifies the certificate for an SSL server. For example, if the IBM Spectrum Protect client initiates the SSL communication with the IBM Spectrum Protect server, the IBM Spectrum Protect client is the SSL client and the server is the SSL server.
| SSL client | SSL server | Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Client | Server | The IBM Spectrum Protect client initiates a communication request with the IBM Spectrum Protect server. The client verifies the certificate. The server provides the certificate. |
| Server (such as a source server) | Server (such as a target server) | The IBM
Spectrum Protect source server
initiates a communication request with the IBM
Spectrum Protect
target server. The source server acts as an SSL client and verifies the certificate that the target
server provides. This type of communication is common during replication processing. |
| Client through a storage agent | Server | The client verifies each certificate when it initiates SSL
communication separately with the IBM
Spectrum Protect server
and the storage agent. When the storage agent communicates with the server by using the SSL communication protocol, the storage agent acts as an SSL client and verifies the certificate that the server provides. The storage agent can be the SSL client and the SSL provider at the same time. |
| Server | LDAP server | The IBM Spectrum Protect server initiates a communication request with the LDAP server. The IBM Spectrum Protect server acts as the SSL client and verifies the certificate that the LDAP server provides. |
| Operations Center | Server | The Operations Center initiates a communication request with the IBM Spectrum Protect server. The Operations Center acts as the SSL client and verifies the certificate that the IBM Spectrum Protect server provides. |
| Reporting | Server | The reporting agent initiates a communication request with the IBM Spectrum Protect server. The Reporting feature acts as the SSL client and verifies the certificate that the IBM Spectrum Protect server provides. |