Editing source code using J2C Doclets
You can add to the Java™ source code in J2C applications to utilize the J2C doclet functionality.
Before you begin
About this task
Supported doclet tags:
The following types of tags are
available to you to add to your Java source code in developing J2C applications:
- J2C tags
- Type Descriptor tags:
Doclet Tag Attributes
Procedure
Results
Example
- In the Enterprise Explorer view, expand your project, expand the Java Resources, and expand the JavaSource section.
- Right click the Java package file (sample.ims, in this case), and select New > Class to launch the New Class wizard.
- Type CCIBuffer as the name of the class. Accept all default settings.
- Click Finish, and the CCIBuffer class opens in the Java editor.
- In the comment section of the CCIBuffer class, add the tag @type-descriptor.message-buffer,
in this way:
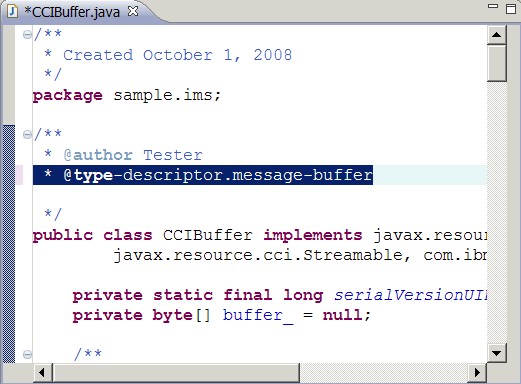
- Press CTRL+S to save the changes. The following code is automatically
generated in the CCIBuffer.java class file:
/* * Created on Oct 13, 2004 * * TODO To change the template for this generated file go to * Window - Preferences - Java - Code Style - Code Templates */ package sample.ims; /** * @author ivyho * * TODO To change the template for this generated type comment go to * Window - Preferences - Java - Code Style - Code Templates * @type-descriptor.message-buffer */ public class CCIBuffer implements javax.resource.cci.Record, javax.resource.cci.Streamable, com.ibm.etools.marshall.RecordBytes { private byte[] buffer_ = null; /** * @generated */ public CCIBuffer() { return; } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#getRecordShortDescription() */ public String getRecordShortDescription() { return (this.getClass().getName()); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#hashCode() */ public int hashCode() { return (super.hashCode()); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Streamable#write(OutputStream) */ public void write(java.io.OutputStream outputStream) throws java.io.IOException { outputStream.write(buffer_); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#setRecordShortDescription(String) */ public void setRecordShortDescription(String shortDescription) { return; } /** * @generated */ public int getSize() { if (buffer_ != null) return (buffer_.length); else return (0); } /** * @generated * @see java.lang.Object#toString */ public String toString() { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(super.toString()); sb.append("\n"); com.ibm.etools.marshall.util.ConversionUtils.dumpBytes(sb, buffer_); return (sb.toString()); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#getRecordName() */ public String getRecordName() { return (this.getClass().getName()); } /** * @generated */ public byte[] getBytes() { return (buffer_); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#clone() */ public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return (super.clone()); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#setRecordName(String) */ public void setRecordName(String recordName) { return; } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Record#equals() */ public boolean equals(Object object) { return (super.equals(object)); } /** * @generated * @see javax.resource.cci.Streamable#read(InputStream) */ public void read(java.io.InputStream inputStream) throws java.io.IOException { byte[] input = new byte[inputStream.available()]; inputStream.read(input); buffer_ = input; } /** * @generated */ public void setBytes(byte[] bytes) { buffer_ = bytes; } }