If you use advanced storage areas for your object stores, you need to choose a replication model that best suits your storage requirements.
Advanced storage areas are designed to be flexible enough to support a wide variety of replication models, including the following common modes: traditional high availability/disaster recovery, remote site, and grid storage. Configuring replicas can sometimes be complex. By using Administration Console for Content Platform Engine, an administrator can configure common and complex custom replication models.
- Traditional high availability/disaster recovery
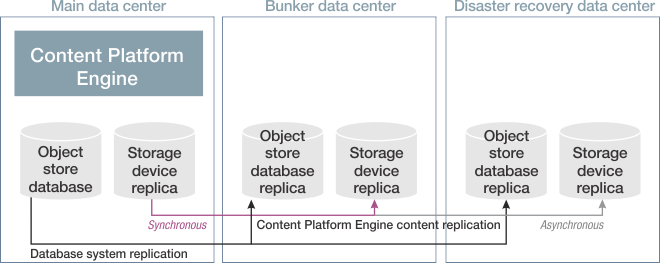
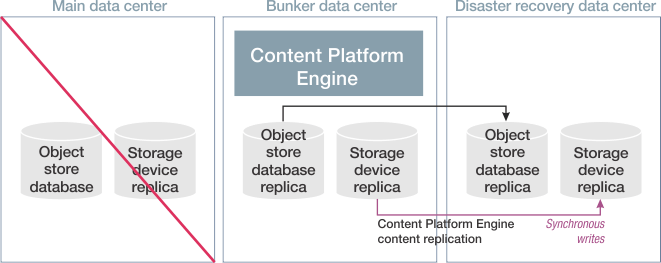
The traditional high availability/disaster recovery replication model consists of an active (main) data center, a passive bunker data center, and a passive disaster recovery data center. The bunker data center and the disaster recovery data center provide database redundancy for content. They are passive in the sense that they are activated only during a failover. The database and content are synchronously replicated from the active data center to the bunker data center, and asynchronously replicated from the active data center to the disaster recovery data center. Bunker data centers and disaster recovery data centers differ only in how they receive database and content (synchronously or asynchronously). If the main data center fails, the bunker data center is started and takes on the role of the main data center. Replication to the disaster recovery data center is synchronous until the main data center is restored.
The following figure illustrates normal operation for this replication model:
The following figure illustrates a failover:
- Remote site
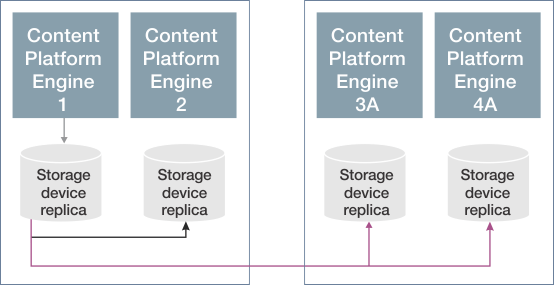
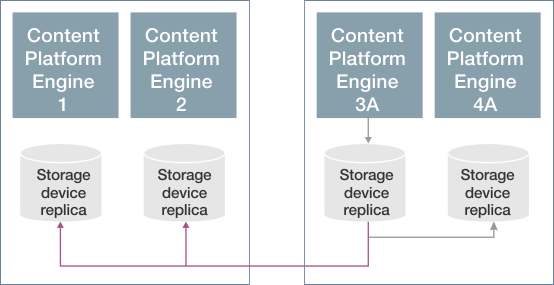
The remote site replication model extends the high availability/disaster recovery model by adding support for replication to and from a replica on a remote site. Content is synchronously written to the local site (Content Platform Engine 1 and 2) and asynchronously written to the remote site (Content Platform Engine 3A and 4A).
The following figure illustrates content being ingested in Content Platform Engine 1:
The following figure illustrates content being ingested in Content Platform Engine 3:
- Grid storage
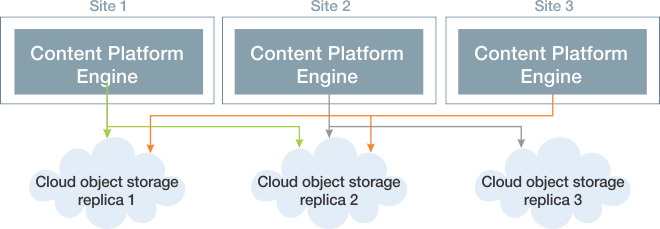
The grid storage model uses cloud storage. The cloud content stores are not tied to any of specific Content Platform Engine site. Content is uploaded to any of the Content Platform Engine instances. Content is synchronously written to two of the three cloud content stores, and asynchronously written to the third store.
The following figure illustrates content being written to the cloud stores: