Data storage in storage pools
Logical storage pools are the principal components in the Tivoli® Storage Manager model of data storage. You can optimize the usage of storage devices by manipulating the properties of storage pools and volumes.
Types of storage pools
The group of storage pools that you set up for the Tivoli Storage Manager server is called server storage. You can define the following types of storage pools in server storage:
- Primary storage pools: A named set of volumes that the server uses to store backup versions of files, archive copies of files, and files that are migrated from client nodes.
- Copy-storage pools: A named set of volumes that contain copies of files that reside in primary storage pools. Copy storage pools are used only to back up the data that is stored in primary storage pools. A copy storage pool cannot be a destination for a backup copy group, an archive copy group, or a management class for space-managed files.
- Active-data storage pools: A named set of storage pool volumes that contain only active versions of client backup data.
Primary storage pools
When you restore, retrieve, recall, or export file data, the requested file is obtained from a primary storage pool. Depending on the type of primary storage pool, the storage pools can be on-site or off-site. You can arrange primary storage pools in a storage hierarchy so that data can be transferred from disk storage to lower-cost storage such as tape devices. Figure 1 illustrates the concept of primary storage pools in Tivoli Storage Manager.
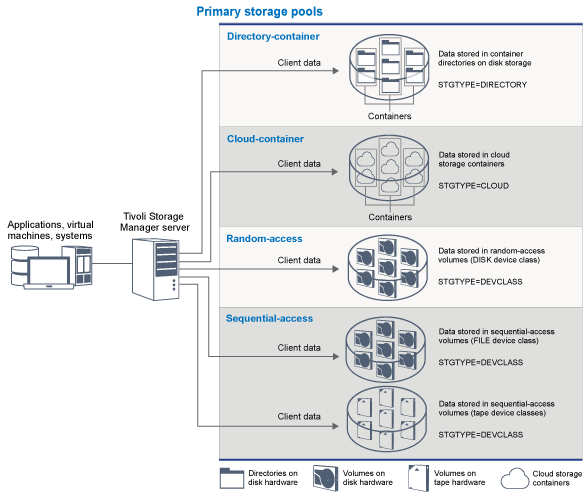
- Directory-container storage pools
A storage pool that the Tivoli Storage Manager server uses to store data in containers in storage pool directories. Data that is stored in a directory-container storage pool can use either inline or client-side data deduplication. In directory-container storage pools, data is deduplicated at the same time that the data is stored. By using directory-container storage pools, you remove the need for volume reclamation, which improves server performance and reduces the cost of storage hardware. You can protect and repair data in directory-container storage pools at the level of the storage pool.
Restriction: You cannot use any of the following functions with directory-container storage pools:- Migration
- Reclamation
- Aggregation
- Collocation
- Simultaneous-write
- Storage pool backup
- Virtual volumes
- Cloud-container storage pools
A storage pool that a server uses to store data in cloud storage. The cloud storage can be on premises or off premises. The cloud-container storage pools that are provided by Tivoli Storage Manager can store data to cloud storage that is object-based. By storing data in cloud-container storage pools, you can exploit the cost per unit advantages that clouds offer along with the scaling capabilities that cloud storage provides. Tivoli Storage Manager manages the credentials, security, read and write I/Os, and the lifecycle for data that is stored to the cloud. When cloud-container storage pools are implemented on the server, you can write directly to the cloud by configuring a cloud-container storage pool with the cloud credentials. The Tivoli Storage Manager server writes deduplicated and encrypted data directly to the cloud. You can back up and restore data or archive and retrieve data directly from the cloud-container storage pool.
You can define the following types of Tivoli Storage Manager cloud-container storage pools:
- On premises
- You can use the on premises type of cloud-container storage pool to store data in a private cloud, for more security and maximum control over your data. The disadvantages of a private cloud are higher costs due to hardware requirements and on-site maintenance.
- Off premises
- You can use the off premises type of cloud-container storage pool to store data in a public cloud. The advantage of using a public cloud is that you can achieve lower costs than for a private cloud, for example by eliminating maintenance. However, you must balance this benefit against possible performance issues due to connection speeds and reduced control over your data.
- Storage pools that are associated with device classes
- You can define a primary storage pool to use the following types of storage devices:
- DISK device class
- In a DISK device type of storage pool, data is stored in random access disk blocks. You can use caching in DISK storage pools to increase client restore performance with some limitations on server processing. Space allocation and tracking by blocks uses more database storage space and requires more processing power than allocation and tracking by volume.
- FILE device class
- In a FILE device type of storage pool, files are stored in sequential volumes for better sequential performance than for storage in disk blocks. To the server, these files have the characteristics of a tape volume so that this type of storage pool is better suited for migration to tape. FILE volumes are useful for electronic vaulting, where data is transferred electronically to a remote site rather than by physical shipment of tape. In general, this type of storage pool is preferred over DISK storage pools.
- ARCHIVEPOOL
- In the STANDARD policy, this storage pool is the destination for files that are archived from client nodes.
- BACKUPPOOL
- In the STANDARD policy, this storage pool is the destination for files that are backed up from client nodes.
- SPACEMGPOOL
- This storage pool is for space-managed files that are migrated from Tivoli Storage Manager for Space Management client nodes.
Copy storage pools
Copy storage pools contain active and inactive versions of data that is backed up from primary storage pools. A directory-container storage pool cannot be used as a copy storage pool. In addition, data from a directory-container storage pool cannot be copied into a copy storage pool. Figure 2 illustrates the concept of copy storage pools in Tivoli Storage Manager.
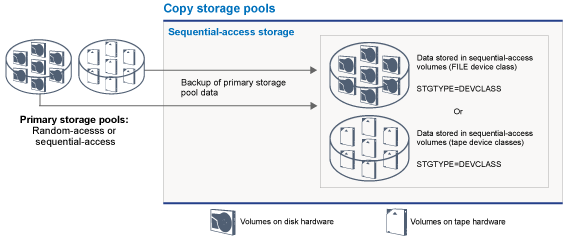
Copy storage pools provide a means of recovering from disasters or media failures. For example, when a client attempts to retrieve a damaged file from the primary storage pool, the client can restore the data from the copy storage pool.
You can move the volumes of copy storage pools offsite and still have the server track the volumes. Moving these volumes offsite provides a means of recovering from an onsite disaster. A copy storage pool can use sequential-access storage only, such as a tape device class or FILE device class.
Active-data storage pools
- Increase the speed of client data restore operations
- Reduce the number of onsite or offsite storage volumes
- Reduce the amount of data that is transferred when you copy or restore files that are vaulted electronically in a remote location
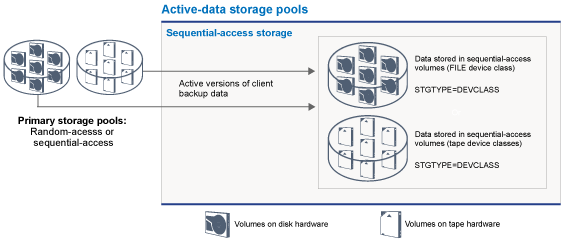
- FILE volumes do not have to be physically mounted
- Client sessions that are restoring from FILE volumes in an active-data pool can access the volumes concurrently, which improves restore performance