How IBM Spectrum Protect nodes are used in a virtual environment
Data Protection for VMware communicates to VMs during backup, restore, and mount operations through IBM Spectrum Protect™ nodes.
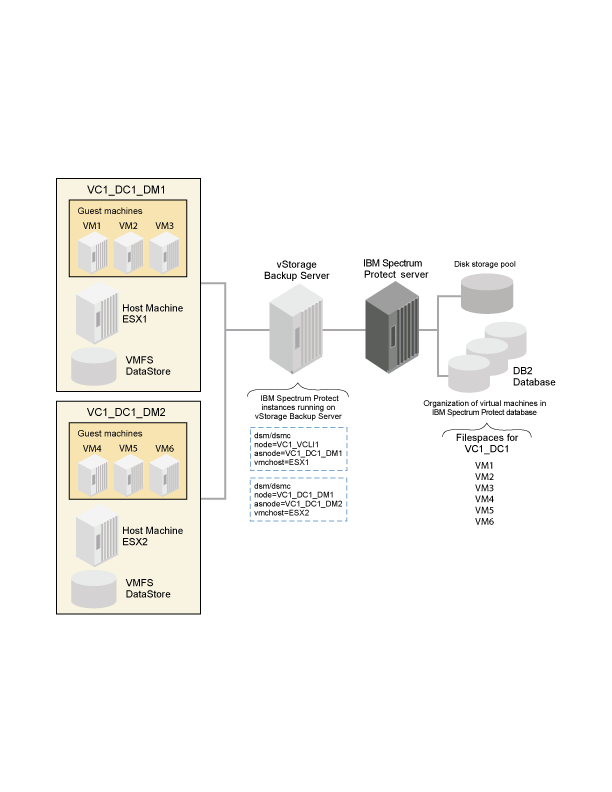
A node represents a system on which the data mover, Data Protection for VMware, or other application client is installed. This system is registered to the IBM Spectrum Protect server. Each node has a unique name (node name) that is used to identify the system to the server. Communication, storage policy, authority, and access to VM data are defined based on a node.
In a Data Protection for VMware vSphere production environment, the most basic node is the data mover node. This node represents a specific data mover that "moves data" from one system to another. In a basic vSphere environment, where VMs are backed up by a single client, the VM data is stored directly under the data mover node.
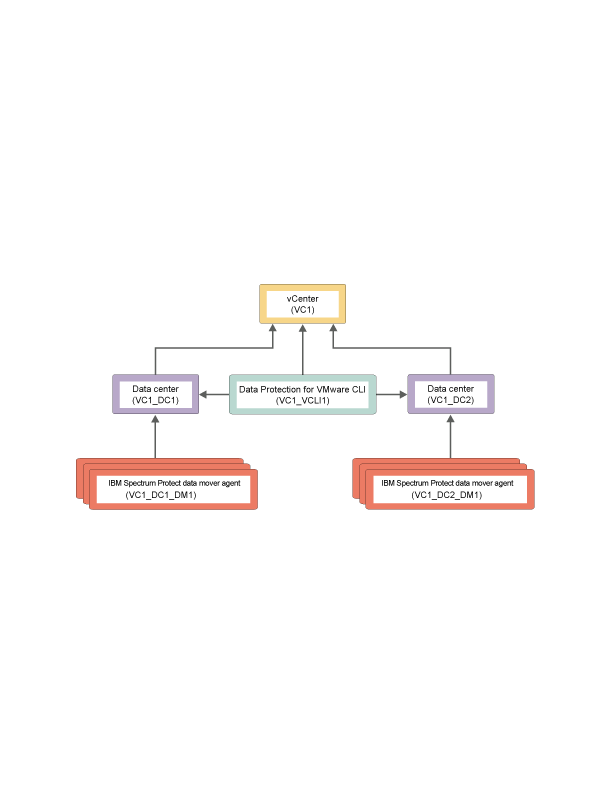
In some scenarios, several data movers are used to back up a complete virtual environment, such as a VMware datacenter. In this scenario, since the backup work is distributed among multiple data movers, the VM data is stored in a shared node (instead of a specific data mover node). This shared node is called the datacenter node. Thus, in this large system vSphere environment, the data mover nodes store VM data into the datacenter node.
In a large vSphere virtual environment, where multiple data movers and datacenter are operative, a third node is used to communicate among the nodes and the IBM Spectrum Protect server. This node is the VMCLI node.
A mount proxy node represents the Linux or Windows proxy system that accesses the mounted VM disks through an iSCSI connection. These nodes enable the file systems on the mounted VM disks to be accessible as mount points on the proxy system. You can then retrieve the files by copying them from the mount points to your local disk. Mount proxy nodes are created in pairs and are required by the datacenter node for each Windows or Linux system that serves as a proxy. To increase the number of available mount points, you can configure a datacenter node to have multiple pairs of mount proxy nodes.
| Node | Description |
|---|---|
| vCenter node | The virtual node that represents a vCenter. |
| datacenter node | The virtual node that maps to a data center. The datacenter nodes hold the data. |
| VMCLI node | The node that connects the Data Protection for VMware command-line interface to the IBM Spectrum Protect server and the data mover node. |
| data mover node | This node performs the data movement.
Important: Data Protection for VMware stores sensitive
information locally on the data mover, and the data mover might also have direct access to VM
storage. Access to the data mover must be protected. Allow only trusted users access to the data
mover system.
|
| mount proxy node | This node represents the Linux or Windows proxy system that accesses the mounted VM disks through an iSCSI connection. These nodes enable the file systems on the mounted VM disks to be accessible as mount points. |