Full-function or Fast Path database PCB statement
The second type of statement in a PSB generation input record specifies a description of a PCB for a DL/I or a Fast Path database.
Although one or more database PCBs are usually included in a PSB, the second type of statement is not always required. For example, a message switching program or conversational message program might not require access to a DL/I database. Therefore, a database PCB is not required.
In a DCCTL environment, database PCBs (except for GSAM PCBs) are not supported, but might be included in the PSBGEN. Application programs that execute in a DCCTL environment and that attempt to use a database PCB will receive an AD status code.
The maximum number of database PCBs that can be defined in a PSBGEN is 2500, including alternate terminal PCBs. This is the maximum value for application programs executing in all IMS region types (MSG, DL/I, and so on).
If a Fast Path secondary index PCB is the only PCB in the PSB, the associated DEDB PCB must be included in the PSB. The minimal DEDB PCB requires a SENSEG statement for the root segment of the associated DEDB database.
The following diagram shows the format for the DL/I database PCB statement.

- 1 label and PCBNAME are mutually exclusive. Use only the label or the PCBNAME= parameter.
- 2 label and PCBNAME are mutually exclusive. Use only the label or the PCBNAME= parameter.
- 3 These operands can be selected in any combination; if G, I, R, and D are selected, use A instead (A = G, I, R, and D combined).

- label
- An optional label used to allow the SBPARM control statement in
the DFSCTL file to reference specific PCBs. If specified, this must
be an alphanumeric 1- to 8-byte character string that is valid for
an assembler language statement. The labels for the PCB statements
within a PSB must be unique.Exception: Do not specify this parameter if PCBNAME= is used.
- TYPE=DB
- Is a required keyword parameter for all DL/I database PCBs.
- DBDNAME= or NAME=
- Is the parameter for the name that specifies the physical or logical
DBD to be used as the primary source of database segments for this
logical data structure. The logical structure, which is defined under
this PCB with one or more SENSEG statements, is the hierarchical set
of data segments to which the associated application program is sensitive.
This logical hierarchy of data segments might or might not exist as
a physical hierarchy. This depends on the relationship of segments
defined by SENSEG statements and the existence of these segments in
one or more databases as defined by their database descriptions (DBDs).
All SENSEG statements that follow this statement and precede the next
PCB or PSBGEN statement must refer to segments defined in the DBD
named in the DBDNAME= or NAME= parameter of this PCB.
The keywords DBDNAME and NAME are synonymous. DBDNAME is more descriptive, and NAME is kept for compatibility with earlier releases.
- DBVER=n
- When database versioning is enabled, specifies the
version number of the database definition (DBD) that this application
program requires.
The numeric value specified must match a version number defined on the DBD and stored in the IMS catalog. Valid values for a database version number are 0 to 2147483647.
If multiple PCBs within a PSB refer to the same database, each PCB must specify the same DBD version number.
- PCBNAME=
- Specifies the name of the PCB. The PCB name must be an alphanumeric,
8-byte character string that follows standard naming conventions.Exception: Do not specify this parameter if the PCB statement includes label.
- PROCOPT=
- Specifies the processing options for the sensitive segments that are declared in
this PCB. You can use these specified options in an associated application program. You can use a
maximum of four options with this parameter. The letters in the parameter have the following meaning:
- A
- All options. By default, PROCOPT=A includes the G (get), I (insert), R (replace), and D (delete) options. PROCOPT=A is the default setting.
- G
- Get option.
- I
- Insert option. By default, PROCOPT=I includes the G (get) option for Fast Path DEDBs; PROCOPT=I does not include the G option for other database types.
- R
- Replace option. By default, PROCOPT=R includes the G (get) option.
- D
- Delete option. By default, PROCOPT=D includes the G (get) option.
- P
- Path calls. Required if command code D is to be used, except for ISRT calls in a batch program that is not sensitive to fields. PROCOPT=P is not required if command code D is used when processing DEDBs. P is used in conjunction with the A (all), G (get), I (insert), D (delete), and L (load) options.
- O
- If the O option is used for a PCB, IMS does not check the
ownership of the segments returned. Therefore, the read without integrity program might get a
segment that has been updated by another program. If the updating program abends and backs out, the
read without integrity program will have a segment that does not exist in the database and never
did. If a segment has been deleted and another segment of the same type has been inserted in the
same location, the segment data, and all subsequent data returned to the application, can be from a
different database record. Therefore, if you use the O option, do not update based on data read with
that option. O must be specified as GO, GON, GONP, GOT, GOTP, or GOP only.
IMS recognizes some of these error types and converts them to abend U0849. However, other conditions that occur under PROCOPT GOx are not detected as having been caused by the read-without-integrity. It is possible to get loops, hangs, and system abends. When using this PROCOPT, carefully consider system design to determine if concurrent update activity is likely to cause higher risk of these kinds of conditions.
- N
- Reduces the number of abends that read-only application programs are subject to. Read-only application programs can reference data being updated by another application program. When this happens, an invalid pointer to the data might exist. If an invalid pointer is detected, the read-only application program abends. By specifying N, you avoid this. A GG status code is returned to the program instead. The program must determine whether to terminate processing, continue processing by reading a different segment, or access the data using a different path. N must be specified as GON, GONH, or GONP.
- T
- Similar to the N option, except that T causes DL/I to automatically retry the operation. If the retry fails, a GG status code is returned to the application program. T must be specified as GOT, GOTH, or GOTP.
- E
- Enables exclusive use of the database or segment by online programs. Used in conjunction with G,
I, D, R, and A.Restriction: For a DEDB, PROCOPT=E is not permitted.
- L
- Load option for database loading (except HIDAM and PHIDAM).
- GS
- Get segments in ascending sequence only (HSAM only). If you specify GS for HSAM databases, they will be read using the Queued Sequential Access Method (QSAM) instead of the basic Sequential Access Method (BSAM) in a DL/I IMS region.
- LS
- Load segments in ascending sequence only (HIDAM, HDAM, PHIDAM, PHDAM). This load option is required for HIDAM and PHIDAM. Because you must specify LS for HIDAM and PHIDAM databases, the index for the root segment sequence field will be created at the time the database is loaded.
- H
- Specifies high-speed sequential processing for the application program that is using a
particular PSB. The following restrictions apply to using PROCOPT=H:
- It can be used for DEDBs only.
- It is allowed on the PCB level and not on the segment level.
- It must be used with other Fast Path processing options.
- A maximum of four PROCOPT options can be specified, including H.
- It can only be specified for BMPs.
- Only one PROCOPT=H PCB per database per PSB is allowed. If a BMP that is using HSSP uses multiple PCBs with PROCOPT=H for the same database within the same PSB, all database calls that are using a PCB other than the first one that is used will receive an FH status code. You can use the NOPROCH keyword on the SETO statement to alleviate this restriction.
- PROCOPT=H cannot be used if PROCSEQD=Fast_Path_index_dbdname is specified.
 PROCOPT=H cannot be used with PROCOPT=GO.
PROCOPT=H cannot be used with PROCOPT=GO. 
If you do not specify the PROCOPT parameter, it defaults to PROCOPT=A. The replace and delete functions also imply the Get function.
A user abend (U8XX) from the retrieve module (DFSDLR00) can occur with PROCOPT=GO if another program updates pointers when this program is following the pointers. A U0800 or U0852 abend can also occur in the VLEXP routine, or in the retrieve module, if an invalid compressed segment is detected. Pointers are updated during the insert and delete functions and during replacement of a variable-length segment. To reduce the number of abends of this type, code the PROCOPT= parameter with an N or a T.
- If any PCBs in the PSB have a PROCOPT of L or LS and either explicitly reference HISAM or HIDAM databases, or implicitly reference INDEX databases, no other PCB in the same PSB can reference any of the databases listed, either explicitly or implicitly, with a PROCOPT other than L or LS. If any PCB in the PSB has a PROCOPT of L or LS and explicitly references a PHIDAM database, no other PCB in the same PSB can reference the PHIDAM database with a PROCOPT of L or LS. The SENSEG statements within that PCB should not contain INDICES= operands.
- If L is specified for a PCB that references a database with multiple data set groups, the PCB should include at least one SENSEG statement for each data set group in the database.
- When the first ISRT call is issued using a PCB with PROCOPT=L,
and the database is using VSAM, the VSAM data set must be empty. If
it is not empty, an open error will result.Recommendation: If the database is using OSAM, use a newly allocated empty data set.
If the data set is not empty, the load will start at the front of the data set, writing over the existing data.
- If the 'O' option is used for a PCB, the SENSEG statement must not specify a PROCOPT of I, R, D, or A.
- An online application program always has exclusive use of the SHSAM or HSAM databases, which are referenced by PCBs in its PSB. No other application programs can be concurrently scheduled to access those same SHSAM or HSAM databases in an online environment.
- If the Online Database Image Copy utility refers to this PCB, the value of PROCOPT= L or LS is invalid. If the database to be copied is the index portion of a HIDAM or PHIDAM database, only PROCOPT=G and PROCOPT=GO are valid. If PROCOPT=E is specified, the Online Image Copy utility will execute with exclusive control of the database, even though the utility does not require the control.
- If the Database Surveyor utility feature refers to this PCB, you must specify PROCOPT=G.
- In the case of concatenated segments, the PROCOPT= parameter governs the logical child segment of the concatenated segment. The logical parent of the concatenated segment is governed by the RULES= parameter of the SEGM statement.
- PROCOPT=E only applies to the database specified in the PCB. To enable exclusive use of a secondary index not explicitly used by the application, add another PCB with PROCOPT=E for the secondary index database.
- SB=
- Specifies which PCBs will be buffered using sequential
buffering (SB). This is an optional parameter. The default is SB=NO,
unless the default option has been modified for Batch and BMPs by
the DFSSBUX0 to SB=COND.
- COND
- Specifies that SB should be activated conditionally. IMS will monitor statistics about the I/O reference pattern of this PCB to the DB data set. If IMS detects a sequential I/O reference pattern and a reasonable activity rate, it will activate SB and acquire the required buffers.
- NO
- Specifies that SB should not be used for this DB PCB.
Tip: For short-running MPPs, Fast Path programs, and CICS® programs, either omit the SB= keyword or specify SB=NO. - KEYLEN=
- The value specified in bytes of the longest concatenated key for
a hierarchic path of sensitive segments that the application program
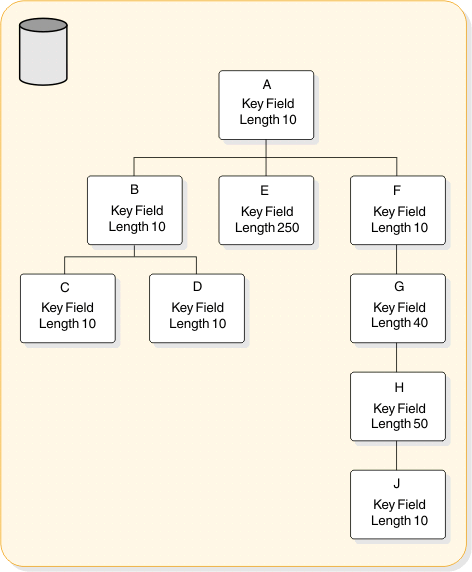
uses in the logical data structure. The following figure shows an IMS database that contains segments
A- H plus segment J. Segments A, B, C, D, F, and J each have a key
field length of 10 bytes. Segment E has a key field length of 250
bytes. Segment G has a key field length of 40 bytes. And Segment H
has a key field length of 50 bytes. The following table shows how
the KEYLEN= will be specified.
Table 1. How a KEYLEN is determined Database hierarchical paths Concatenated key length paths A+B+C= 30 bytes A+B+D= 30 bytes A+E= 260 bytes A+F+G+H+J= 120 bytes A KEYLEN=260 bytes would be specified
For a non-terminal-related MSDB without terminal-related keys, the value must be greater than or equal to the value of the BYTES parameter of the sequence field in the DBD generation and be from 1 to 240 bytes.
For a terminal-related MSDB (using the LTERM name as a key), this value must be 8.
- POS=
- Specifies single or multiple positioning for the logical
data structure. Single or multiple positioning provides a functional
variation in the call.
The performance variation between single and multiple positioning is insignificant. HSAM does not support multiple positioning.
POS=SINGLE or S is the default.
Exception: For DEDBs having more than two dependent segments, the default is POS=MULTPLE or M.Coding a POS value on the PCB statement for a DEDB will not override the default that is selected based on the number of dependent segments.
- PROCSEQ=
- Specifies the name of a secondary index that is
used to process the database named in the DBDNAME parameter through
a secondary processing sequence. The parameter is optional. It is
valid only if a secondary index exists for this database. If this
parameter is used, subsequent SENSEG statements must reflect the secondary
processing sequence hierarchy of segment types in the indexed database.
For example, the first SENSEG statement must name the indexed segment
with a PARENT=0 parameter.
full_function_index_dbname must be the name of a secondary index DBD.
For a secondary processing sequence, processing options L and LS are invalid. Inserting and deleting the index target segment and any of its inverted parents is not allowed. When the blocks are built, if the processing option for these segments includes I or D, a warning message indicates that the processing option has been changed to reflect this restriction.
- PROCSEQD=
- Specifies the name of the secondary index database
to be used to access the segments in the primary DEDB database. The
parameter is optional. It is valid only if a secondary index exists
for this database. If this parameter is used, subsequent SENSEG statements
must be coded in the physical sequence of the primary DEDB. The minimum
SENSEG statements to be coded are those in the path from the physical
root segment, to the index segment (also called the target segment).
For partitioned secondary index databases, Fast_Path_index_dbname must be the first dbdname listed in the LCHILD statement.
For a secondary processing sequence, processing options L and LS are invalid. Inserting and deleting the index target segment and any of its inverted parents is not allowed. When the blocks are built, if the processing option for these segments includes I or D, a warning message indicates that the processing option has been changed to reflect this restriction.
When user partitioning is requested for HISAM or SHISAM secondary index databases, the PROCSEQD= parameter specifies the name of the first partition database in the user partition group as defined in the NAME= parameter on the LCHILD statement in the primary DEDB database DBD. The user partition selection exit in the PSELRTN= parameter on the XDFLD statement determines the actual partition database to use based on the secondary index key value.
- PSELOPT=
- Indicates how user partition databases in a user
partition group are logically grouped for qualified GN calls with
no SSA processing before the end of data is reached on the user partition
databases. User partition databases are defined as part of a user
partition group in the NAME= parameter on the LCHILD statement. This
parameter applies to Fast Path secondary index databases only.
The PSELOPT= parameter can also be specified on the XDFLD statement. There is no default for the PSELOPT= parameter on the PCB statement with the PROCSEQD= parameter, whereas PSELOPT=MULT is the default for the PSELOPT= parameter on a XDFLD statement.
If the PSELOPT= parameter is specified on both the XDFLD statement and the PCB statement with the PROCSEQD operand, the PSELOPT= parameter on the PCB statement takes precedence.
- MULT
- Indicates the selected user partition and its subsequent user partition databases in a user data partition group as they are physically defined in the NAME= parameter on the LCHILD statement of the primary DEDB database DBD. PSELOPT=MULT is the default for the PSELOPT= parameter on a XDFLD statement.
- SNGL
- Indicates that only the selected user partition database is used.
- ACCESS=
- Specifies whether the secondary index database
is to be used to access its primary DEDB database or the secondary
index database is to be processed as a separate logical database.
- DB
- Specifies that the primary DEDB database is accessed using its secondary index sequence. ACCESS=DB is the default.
- (INDEX,VSAM) | (INDEX,SHISAM)
- Specifies that one or more user partition databases in a user
partition group are accessed as a separate logical database.
Specify ACCESS=(INDEX,VSAM) for a HISAM secondary index database on the DBD statement for a Fast Path secondary index database.
Specify ACCESS=(INDEX,SHISAM) for a SHISAM secondary index database on the DBD statement for a Fast Path secondary index database.
- VIEW=MSDB
- Is used to specify the MSDB commit view. Your
existing applications can use either MSDB commit view or the default
DEDB commit view. To use the MSDB commit view for DEDBs, specify VIEW=MSDB
on the statement. If you do not specify VIEW=MSDB, the DEDB will use
the DEDB commit view. No changes to any existing application programs
are required to migrate your MSDBs to DEDBs.
If you issue a REPL call with a PCB that specifies VIEW=MSDB, the segment must have a key. This includes any segment in a path if command code 'D' is specified. Otherwise, status AM is returned.
- LIST=
- Specifies whether the named PCB is included in the
PCB list passed to the application program at entry. Specify YES to
include a named PCB in the PCB list. Specify NO to exclude a named
PCB from the PCB list. YES is the default.
To exclude a PCB from the PCB list, you must assign the PCB a name with either the label or PCBNAME= parameter. You can specify LIST=NO if an application program does not need a PCB's address.
- EXTERNALNAME=
- An optional alias for the PCB label or the PCBNAME= parameter. Java™ application programs use the
external name to refer to the PCB.
Specify an external name as a 1- to 128-character uppercase alphanumeric string. An external name can include underscore characters.
The external name must be unique within a PSB.
When EXTERNALNAME is not specified, the default external name is either the PCB label or the PCBNAME, whichever has been specified.
If no PCB label or PCBNAME is specified, EXTERNALNAME defaults to blanks.
Restriction: External names cannot be reserved SQL keywords or begin with DFS.If the EXTERNALNAME parameter is not specified and a reserved SQL keyword is specified in the NAME parameter, EXTERNALNAME accepts the NAME value as the default external name after appending
_SCH
to the NAME value. - REMARKS=
- Optional user comments. A 1- to 256-character field.
If your comments contain special characters, such as commas or blank spaces, enclose the full comment string in single quotation marks.
The value specified on the REMARKS keyword cannot contain the following characters:- Single quotation marks, except when they are used to enclose the full comment string. If
a single quotation mark is entered before the end of the full comment string, the remainder
of the comment string is truncated. The following examples show correct and incorrect
usages of single quotation marks on the REMARKS keyword:
- CORRECT
REMARKS='These remarks apply to the XYZ application'- INCORRECT
REMARKS='These remarks apply to the 'XYZ' application'
- Double quotation marks.
- Less than (< ) symbols.
- Greater than ( >) symbols.
- Ampersands (&).
- Single quotation marks, except when they are used to enclose the full comment string. If
a single quotation mark is entered before the end of the full comment string, the remainder
of the comment string is truncated. The following examples show correct and incorrect
usages of single quotation marks on the REMARKS keyword:
