Abstract for RACF Security Server Diagnosis Guide
This document contains information about diagnosing problems on the IBM® RACF® Security Server for z/VM®.
Though this document is specific to z/VM, there are references to z/OS®. These references are only applicable when sharing a RACF database with a z/OS system.
Intended Audience
This document is for anyone who diagnoses problems that appear to be caused by RACF and for RACF system programmers who intend to use the BLKUPD command to correct problems in the RACF database.
- Understand basic system concepts and the use of system services
- Code in assembler language and read assembler and linkage editor output
- Understand the commonly-used diagnostic tasks and aids, such as message logs, system dumps, and Dump Viewing Facility
- Understand the externals for RACF.
- The problem type, such as an abend
- An indication that the problem was caused by RACF.
If you do not have this data, see your system diagnosis guide and perform its procedures.
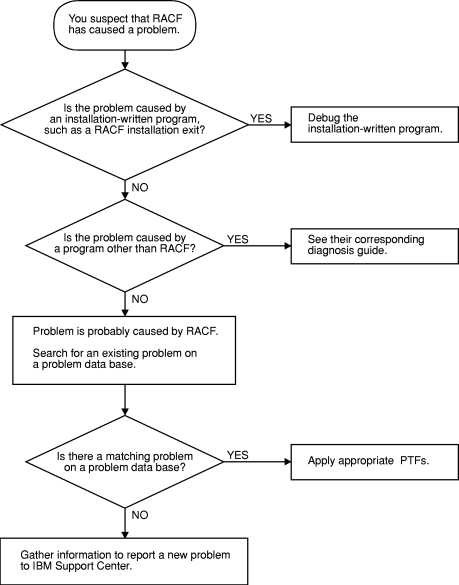
Use this document to diagnose problems in RACF only. If the problem is not caused by RACF, return to your system diagnosis guide to identify the failing component or program product.
Use this document to diagnose problems in RACF as follows:
- Identify the problem type.
- Collect problem data.
- Analyze the problem data to develop symptoms.
- Develop search arguments, search problem-reporting databases, and request the problem fix if the problem has been reported before. If not, continue diagnosis.
- Collect additional problem data.
- Analyze the problem data to isolate the problem.
- Report the problem to IBM if assistance is needed or if the problem is new.
Planning for Problem Diagnosis
- Properly install and operate of RACF so that you get adequate problem data (such as messages and dumps) when problems occur.
- Perform timely and complete backups of the RACF database.
- Have access to a RACF user with the SPECIAL attribute.
- Reserve a RACF user ID
with the SPECIAL attribute for use only after logon problems are
resolved.
For example, if all users logging on are, through an error, revoked when logging on, then the system security administrator could also be revoked when logging on. After the problem is corrected, the system security administrator could then log on with the user ID that is still active and activate the other user IDs.
- Prepare to use the following debugging techniques (at least):
- Obtain messages that have been sent to the system console or the security console
- Check the console log of the RACF service machines.
- Prevent common problems by using RACF macros and utilities. See the recommendations in Common Usage Problems with RACF Macros and Utilities.
- Correct any problems that were caused while using RACF profiles and options. See z/VM: RACF Security Server Security Administrator's Guide for more information.